
How to Manage Systemic Nutrient Depletion
In today’s fast-paced environment, it’s easy to overlook the importance of proper nutrition. The consequences of systemic nutrient depletion can significantly impact your overall health and well-being. Systemic nutrient depletion is when the body experiences a deficiency of essential nutrients necessary for optimal physiological functions. This depletion can occur due to various factors, including inadequate dietary intake, poor absorption, increased nutrient demands (such as during periods of stress or illness), and certain medications that interfere with nutrient absorption or use. When the body consistently lacks vital vitamins, minerals, and other essential compounds, it can lead to various health issues and impact your overall well-being.
Understanding the Importance of Nutrients
Nutrients play a vital role in maintaining various bodily functions. They are essential for growth, development, and overall health maintenance. There are six main categories of nutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water. Each nutrient has specific functions; a deficiency in any of these can lead to various health problems.
- Focus on a rich assortment of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to ensure a broad spectrum of essential nutrients.
- Favor high fiber and lean protein sources like poultry and fish while incorporating healthy fats like avocados.
- Adequate hydration is vital, and limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive salt intake is equally critical.
Embracing these dietary guidelines significantly diminishes the risk of systemic nutrient depletion and promotes healthier eating habits.
The Impact of Nutrient Deficiency on Overall Health
When the body lacks essential nutrients, it struggles to perform its necessary functions.

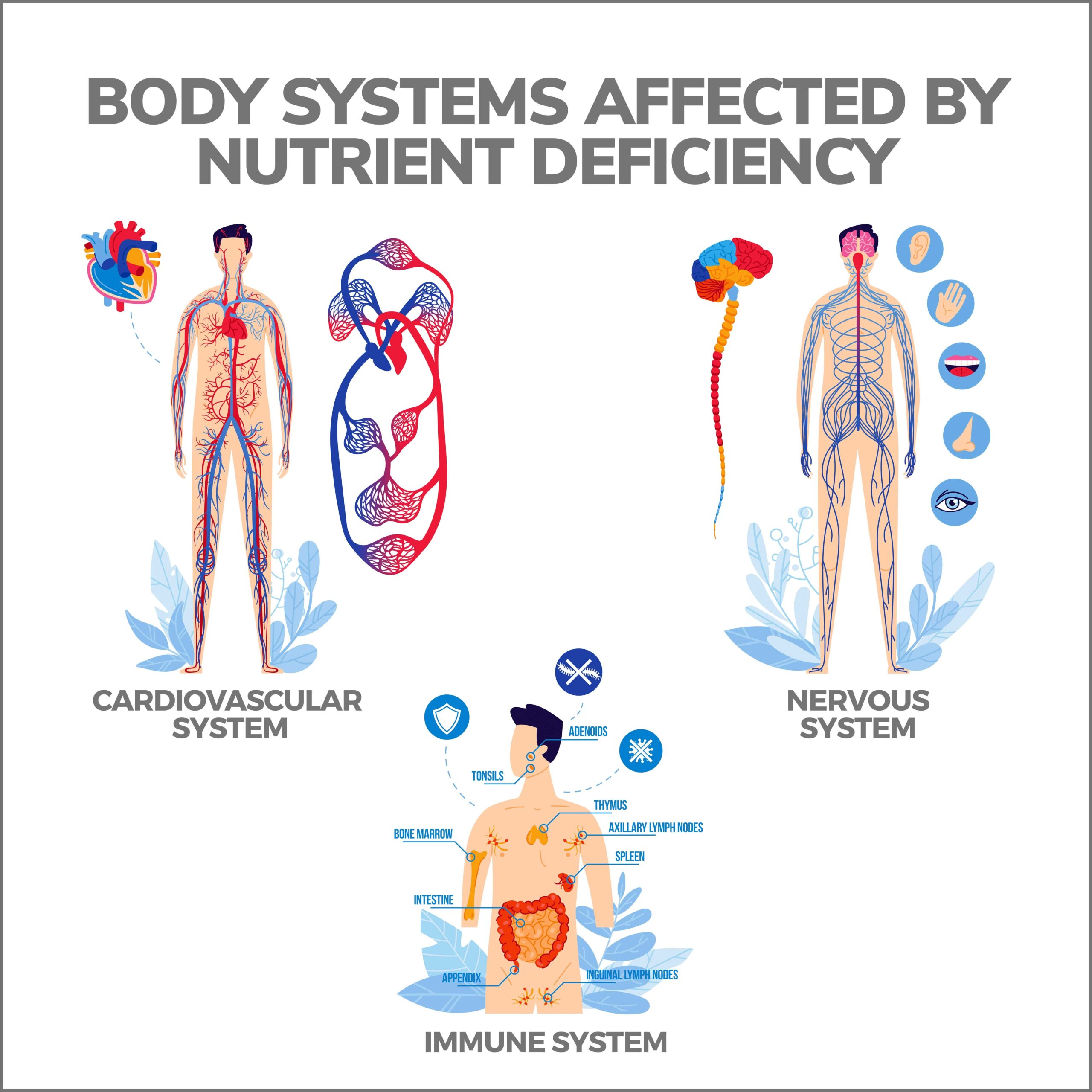
Nutrient deficiencies can affect various systems in the body, including the immune system, cardiovascular system, nervous system, and musculoskeletal system:
- Immune System: Relies on adequate nutrient intake to function optimally. The body’s ability to fight infections and diseases is compromised without enough nutrients. This can lead to frequent illnesses, slower healing, and a weakened immune response.
- Cardiovascular System: Also relies on nutrients for proper function. Nutrient deficiencies can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, such as hypertension, high cholesterol, and heart disease. Inadequate intake of certain nutrients, such as calcium and vitamin D, can weaken bones and increase the risk of osteoporosis.
- Musculoskeletal System: Requires proper nutrition for growth, repair, and maintenance of muscles and bones. Nutrient deficiencies can lead to muscle weakness, fatigue, and poor growth in children.
- Nervous System: Nutrient deficiencies can impact cognitive function, mood, and overall mental well-being. A lack of essential nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids and B vitamins, can contribute to poor concentration, memory problems, and even depression or anxiety.
Causes and Consequences of Systemic Nutrient Depletion
A variety of factors can cause systemic nutrient depletion. One of the primary causes is a poor diet lacking in essential nutrients. Fast food, processed foods, and a diet high in sugar and unhealthy fats can contribute to nutrient deficiencies. Certain medical conditions, such as malabsorption disorders or chronic illnesses, can impair the body’s ability to absorb and utilize nutrients effectively.
The consequences of systemic nutrient depletion can be far-reaching. Nutrient deficiencies can weaken the immune system, leaving the body more susceptible to infections and diseases. They can also impair cognitive function, leading to poor concentration, memory problems, and even mental health issues. Inadequate nutrient intake can also impact physical health, resulting in fatigue, muscle weakness, and poor growth in children.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Nutrient Depletion
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of nutrient depletion is crucial for timely intervention. While the specific symptoms may vary depending on the nutrient deficiency, some common signs should not be ignored. Fatigue and weakness are often early warning signs of nutrient depletion. If you find yourself constantly tired, even after appropriate rest, it could be a sign that your body lacks essential nutrients.
Other common symptoms include frequent illnesses or infections, slow wound healing, poor concentration and memory, hair loss, brittle nails, muscle cramps, mood swings, and changes in appetite or weight. If you experience any of these symptoms, consult GastroMD for a comprehensive evaluation and proper diagnosis.
How to Identify and Address Nutrient Deficiencies
Identifying nutrient deficiencies requires a combination of medical evaluation and self-awareness. An inclusive blood test can provide valuable information about your nutrient levels. Your gastroenterologist will analyze the results and identify any deficiencies that need to be addressed.
Beyond medical evaluation, self-awareness of your dietary habits and lifestyle choices is crucial. Keeping a food diary can help you identify patterns and potential nutrient gaps in your diet. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential. Consult a registered dietitian who can provide personalized guidance and help you create a nutrient-dense meal plan.
In some cases, nutrient supplementation may be necessary to address deficiencies, but talking with your GastroMD physician before starting any supplements is essential. We will recommend the appropriate dosage and guide you on the safest and most effective treatment options.
Long-Term Effects of Systemic Nutrient Depletion
If left untreated, systemic nutrient depletion can have long-term consequences for overall health. Chronic nutrient deficiencies can lead to the development of various diseases and conditions. For example, vitamin D deficiency can increase the risk of osteoporosis and bone fractures. Iron deficiency can lead to anemia, resulting in fatigue, weakness, and poor cognitive function.
Inadequate intake of essential nutrients can also contribute to the development of chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. The body relies on a balanced intake of nutrients to function optimally and maintain a healthy immune system. The body’s defenses weaken without proper nutrition, making it more susceptible to infections and diseases.
Contact Us
Recognizing the importance of nutrients and maintaining a balanced diet is essential to preventing nutrient deficiencies. Regular medical evaluation, self-awareness of dietary habits, and timely intervention are key to addressing and treating nutrient depletion. By making informed food choices and staying physically active, individuals can take control of their nutrition and reduce the risk of systemic nutrient depletion. Prevention is undoubtedly better than cure, and investing in good nutrition lays the foundation for long-term health and well-being.
At GastroMD, we prioritize your well-being. For personalized guidance on preventing and addressing nutrient deficiencies, schedule your appointment with us today and embark on a journey to a healthier, more vibrant you.



