
Celiac Disease Awareness Month: Everything to Know About the Disease
May is Celiac Disease Awareness Month, and we are seizing the opportunity to educate and raise awareness about the impact of gluten-free living. Celiac disease is a medically diagnosed autoimmune disorder that affects millions worldwide. Defined by a severe intolerance to gluten, celiac disease can wreak havoc on the body’s digestive system, leading to a range of symptoms from mild discomfort to debilitating illness.
What is Celiac Disease?
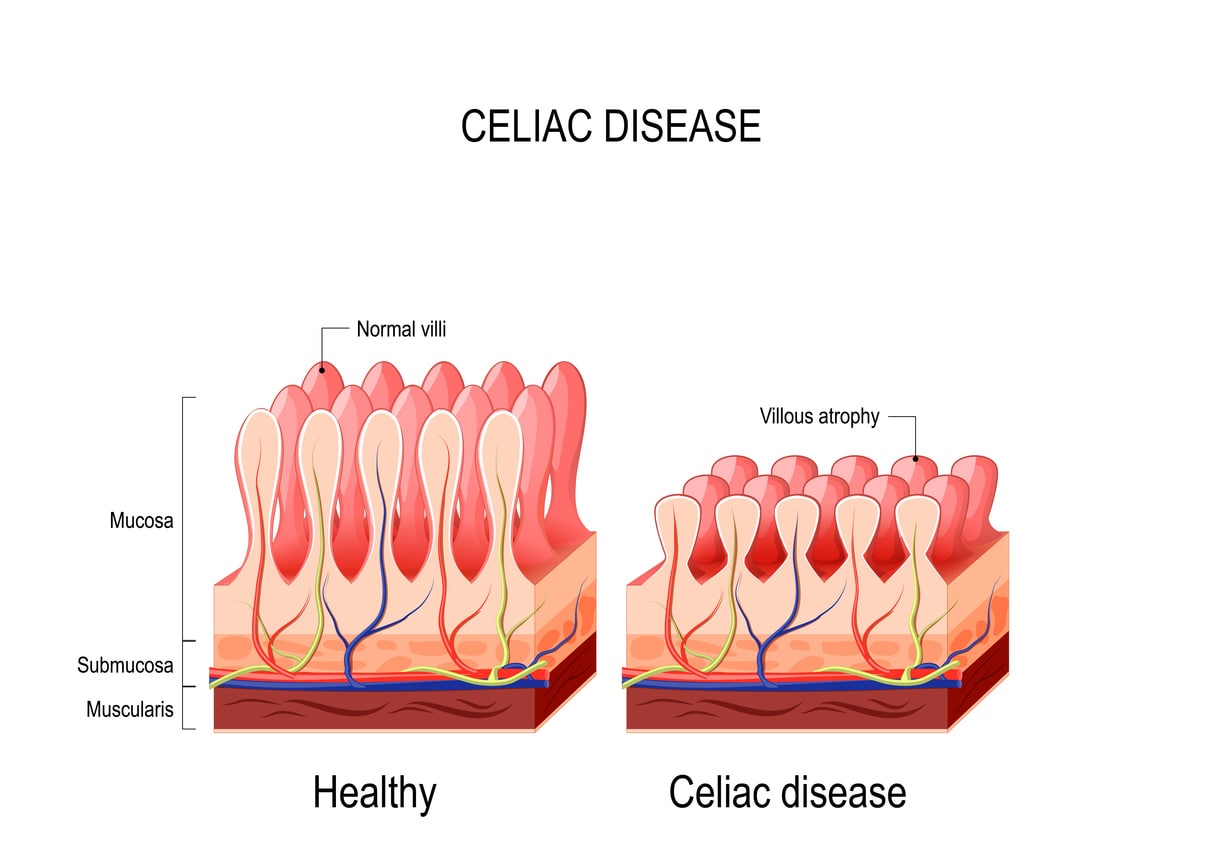
Celiac disease is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by a hypersensitive immune response to gluten, a protein commonly found in grains like wheat, barley, and rye. Gluten is commonly used in baking and food production because it provides elasticity to dough, allowing it to rise, hold its shape during baking, and facilitate the binding of ingredients. When people with celiac disease consume gluten, their immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the small intestine, leading to inflammation and damage to the small intestine’s lining. This damage interferes with the absorption of nutrients from food, leading to symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and fatigue. Celiac disease can also manifest with non-gastrointestinal symptoms, including malnutrition, osteoporosis, infertility, and an increased risk of other autoimmune disorders and certain cancers. Those with celiac disease must strictly avoid gluten-containing foods to prevent these adverse effects and manage their condition effectively.
Symptoms of Celiac Disease
Celiac disease can manifest in a variety of ways, and its symptoms can vary from person to person. Some common symptoms include the following:
- Digestive Issues: Individuals with celiac disease often experience abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, constipation, and nausea after consuming gluten-containing foods.
- Fatigue: Chronic fatigue and weakness are common symptoms of celiac disease, even with adequate rest.
- Anemia: Celiac disease can lead to iron deficiency anemia due to malabsorption of nutrients like iron.
- Skin Rash: Dermatitis herpetiformis, a blistering skin rash, may occur in some individuals with celiac disease.
- Joint Pain: Celiac disease can cause inflammation and joint pain resembling arthritis symptoms.
It is important to note that celiac disease is often termed a “silent” condition because certain people may have minimal or no noticeable symptoms despite significant damage to their small intestine. This can make diagnosing challenging, as patients may not seek medical attention until complications arise or the condition is detected through screening tests. In most cases, celiac disease does manifest noticeable symptoms, particularly upon gluten consumption.
Causes and Risk Factors of Celiac Disease
The exact cause of celiac disease is still unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Individuals with a family history of celiac disease are at a higher risk of developing the condition, as there is a strong genetic component. Certain autoimmune disorders, such as type 1 diabetes and autoimmune thyroid disease, are commonly associated with celiac disease. Environmental factors, such as the introduction of gluten into an infant’s diet before the age of six months, may also play a role in the development of celiac disease.
Managing & Treating Celiac Disease
To effectively manage celiac disease, strict adherence to a gluten-free diet is essential, eliminating all gluten sources from your diet, including wheat, barley, and rye. This can be challenging, as gluten can be found in various foods, beverages, and even non-food products. It is important to carefully read labels and educate yourself about hidden sources of gluten. Many gluten-free alternatives are now available, making it easier to adhere to a gluten-free lifestyle. Working with a registered dietitian specializing in celiac disease can provide valuable guidance and support in navigating the gluten-free diet.
Unfortunately, there is no cure for celiac disease. The only treatment option available is adopting a strict gluten-free diet. This can significantly improve symptoms and prevent long-term complications. Individuals may sometimes require additional medical intervention to manage specific symptoms or complications. For example, if a person with celiac disease has severe malabsorption or nutrient deficiencies, they may require vitamin and mineral supplements. Working closely with a healthcare team to develop an individualized treatment plan based on your specific needs is essential.

Living with Celiac Disease
Living with celiac disease can present unique challenges, but with the right strategies, you can lead a fulfilling life. Here are some tips for managing celiac disease:
- Educate Yourself: Learn about the condition, its symptoms, and how to navigate a gluten-free lifestyle. Knowledge is power when it comes to managing celiac disease.
- Seek Support: Connect with support groups, both online and offline, where you can share experiences, ask questions, and receive support from others who understand what you’re going through. Resources such as the Celiac Disease Foundation can provide valuable assistance, information, and insights.
- Plan Ahead: When dining out or traveling, plan ahead and communicate your dietary needs to ensure that gluten-free options are available. Pack gluten-free snacks and meals if necessary.
- Be Cautious of Cross-contamination: Even a small amount of gluten can trigger a reaction in those with celiac disease. Take precautions to avoid cross-contamination in your kitchen and when eating out.
Contact Us
Celiac disease is a complex autoimmune disorder that requires lifelong management. By understanding its symptoms, causes, and risk factors, you can take proactive steps to seek a diagnosis and begin managing the condition. Adopting a gluten-free diet and implementing coping strategies can significantly improve the quality of life for those with celiac disease. Remember, knowledge and support are key in navigating the challenges of living with this silent health condition.
If you suspect you may have celiac disease or have been recently diagnosed, contact GastroMD today. We’re here to help you thrive and provide support throughout your journey, so don’t hesitate to reach out for the assistance and care you deserve.



