
Gut-Friendly Holiday Meals
Hepatology is a branch of medicine dedicated to the study and treatment of liver diseases. It plays a crucial role in understanding and managing conditions that affect one of the body’s most vital organs. The liver has many essential functions. It detoxifies harmful substances, synthesizes proteins, and regulates metabolism. With the rise in liver issues like hepatitis and fatty liver, the importance of hepatology is clear.
Understanding Hepatology and the Role of Hepatologists
Hepatology focuses on liver health and the various diseases that can affect this crucial organ. Hepatologists are specialized doctors who diagnose and manage liver conditions. They provide insights into many liver-related issues, ranging from common ailments, like hepatitis, to complex disorders, such as cirrhosis and liver cancer. As liver disease continues to be a growing concern worldwide, the role of hepatologists in early diagnosis, prevention, and treatment is more vital than ever.
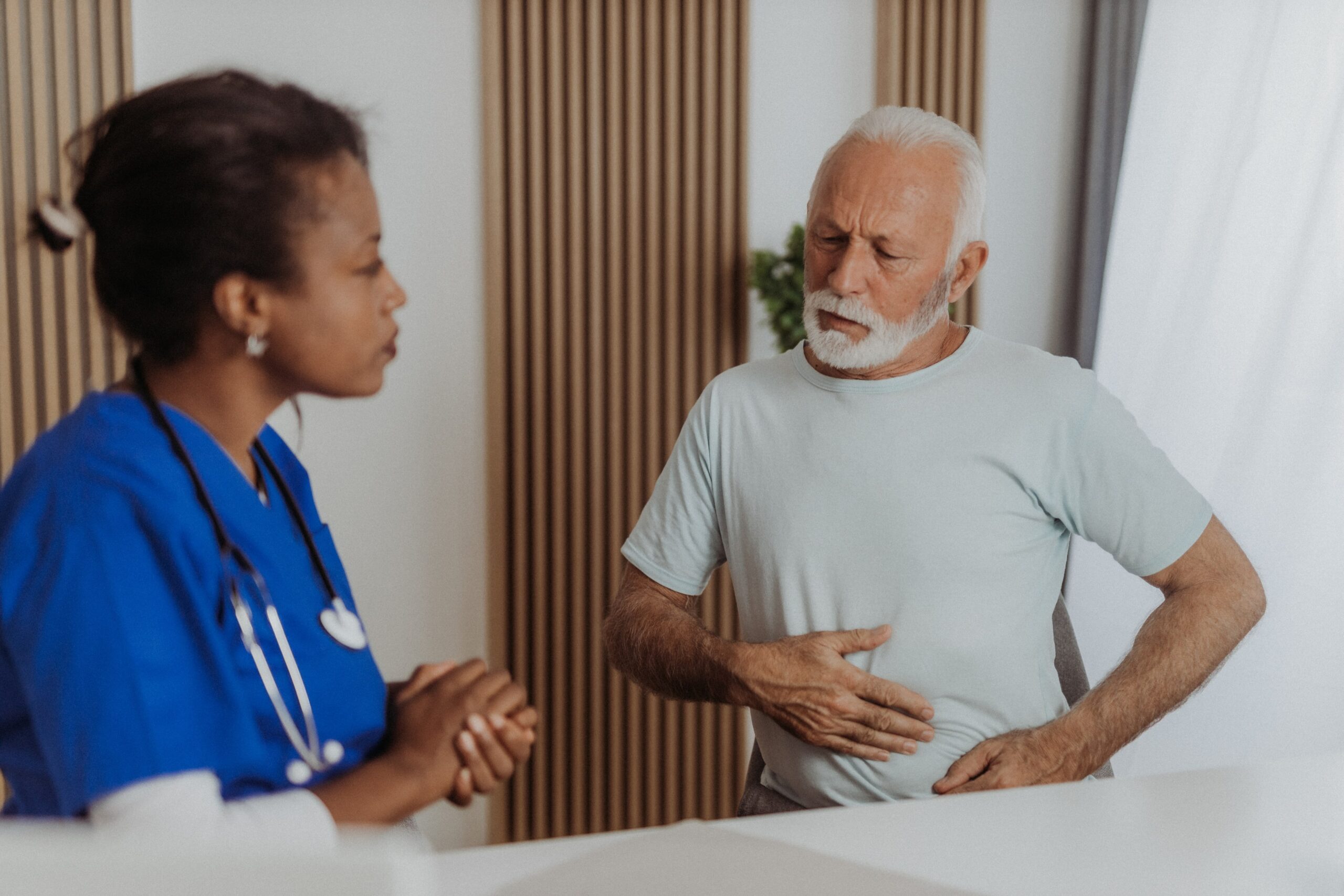
Symptoms of Liver Disease
Recognizing the signs of liver disease early is crucial for timely treatment and better outcomes. Liver disease can present in many ways, often with subtle symptoms that might go unnoticed in the early stages. Here are some common symptoms that may indicate liver issues:
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes caused by high bilirubin levels in the blood.
- Abdominal Pain and Swelling: Discomfort or bloating in the upper right abdomen, often linked to liver inflammation or enlargement.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness or weakness, a common symptom of many liver disorders.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Frequent nausea or vomiting, which may indicate liver dysfunction affecting digestion.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing weight without a clear cause can be a sign of liver disease.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice for an accurate diagnosis.
Key Functions of the Liver
The liver is essential for maintaining overall health. It detoxifies harmful substances and metabolizes food nutrients. It produces bile for digestion and proteins for blood clotting and immune function. The liver regulates blood sugar and stores vitamins and minerals, providing the body with energy when needed. Given the liver’s complex and vital functions, liver dysfunction can lead to significant health problems.
Common Liver Diseases and Disorders
Hepatology addresses a wide range of liver conditions, from acute infections to chronic diseases. Understanding these disorders is crucial for early detection and effective management. Some of the most common liver diseases and disorders include:
- Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver caused by viral infections or alcohol consumption. Hepatitis can lead to severe complications, including cirrhosis and liver cancer.
- Fatty Liver Disease: The buildup of excess fat in liver cells, which can be either non-alcoholic (related to obesity) or alcohol related. If untreated, fatty liver disease can progress to inflammation and liver damage.
- Cirrhosis: Scarring of the liver due to long-term damage, often caused by chronic alcohol abuse or hepatitis. Cirrhosis leads to declining liver function and can result in life-threatening complications.
- Liver Cancer: A malignant tumor that can develop as a result of chronic liver diseases, such as hepatitis and cirrhosis. It is often diagnosed at advanced stages, making early detection critical.
- Liver Fibrosis: The accumulation of scar tissue in the liver caused by chronic inflammation. If left untreated, liver fibrosis can progress to cirrhosis, leading to further complications.
By understanding these conditions, you can be more proactive in managing your liver health and seeking treatment when necessary.
Identifying the Need for Hepatology
Diagnosing the need for hepatology involves a comprehensive evaluation of a patient’s medical history, symptoms, and risk factors for liver disease. Doctors may start with a physical exam. They will check for existing conditions like obesity, diabetes, or a history of alcohol use or viral infections. Blood tests are often used to assess liver function and identify liver disease or infections.
Imaging studies, like ultrasound or MRI, can help visualize the liver and detect abnormalities. In some cases, a liver biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and determine the severity of any liver damage. These methods ensure timely referrals to hepatologists for liver issues.
Treatment Approaches in Hepatology
Hepatology offers a variety of treatment options to manage liver diseases, depending on the specific condition and its severity. These treatments aim to improve liver function, reduce symptoms, and prevent complications. Common treatment approaches in hepatology include:
- Medications: Antiviral drugs for hepatitis, symptom-relieving medications, and drugs that can slow the progression of cirrhosis.
- Lifestyle Changes: Recommendations to improve liver health, including dietary changes, regular exercise, and reducing alcohol consumption, especially in cases of fatty liver disease.
- Surgical Interventions: Procedures like liver biopsies, tumor removal, and endoscopic interventions to manage complications such as varices in cirrhosis.
- Liver Transplantation: For advanced liver disease, a liver transplant may be necessary to restore liver function.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Regular blood tests and imaging help monitor the progression of liver disease and ensure that treatment plans are adjusted as needed.
Each patient’s treatment plan will depend on their specific condition and the stage of their liver disease, and hepatologists play a critical role in providing personalized care.

Preventative Measures
Preventative measures in hepatology focus on reducing the risk of liver disease and promoting overall liver health. Key strategies include:
- Vaccination: Vaccines for hepatitis A and B can prevent viral infections that cause liver damage.
- Healthy Diet and Exercise: Maintaining a balanced diet and regular physical activity can prevent conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Alcohol Moderation: Limiting alcohol intake can significantly reduce the risk of developing liver diseases, such as alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
- Safe Practices to Avoid Infections: Practicing good hygiene, safe sex, and avoiding needle-sharing can prevent the spread of hepatitis infections.
- Regular Health Screenings: Routine blood tests and liver function screenings help detect early signs of liver disease, allowing for prompt intervention.
You can protect your liver and prevent liver diseases by taking preventative steps.
Contact Us for Care
Hepatology is important for keeping your liver healthy and treating liver diseases. Early detection and specialized care are key as new treatments are developed. Staying informed and taking care of your liver can help improve your overall health. If you have concerns about your liver or symptoms, schedule an appointment with our team at GastroMD. We provide thorough evaluations, expert diagnoses, and personalized treatment plans to support your liver health.



