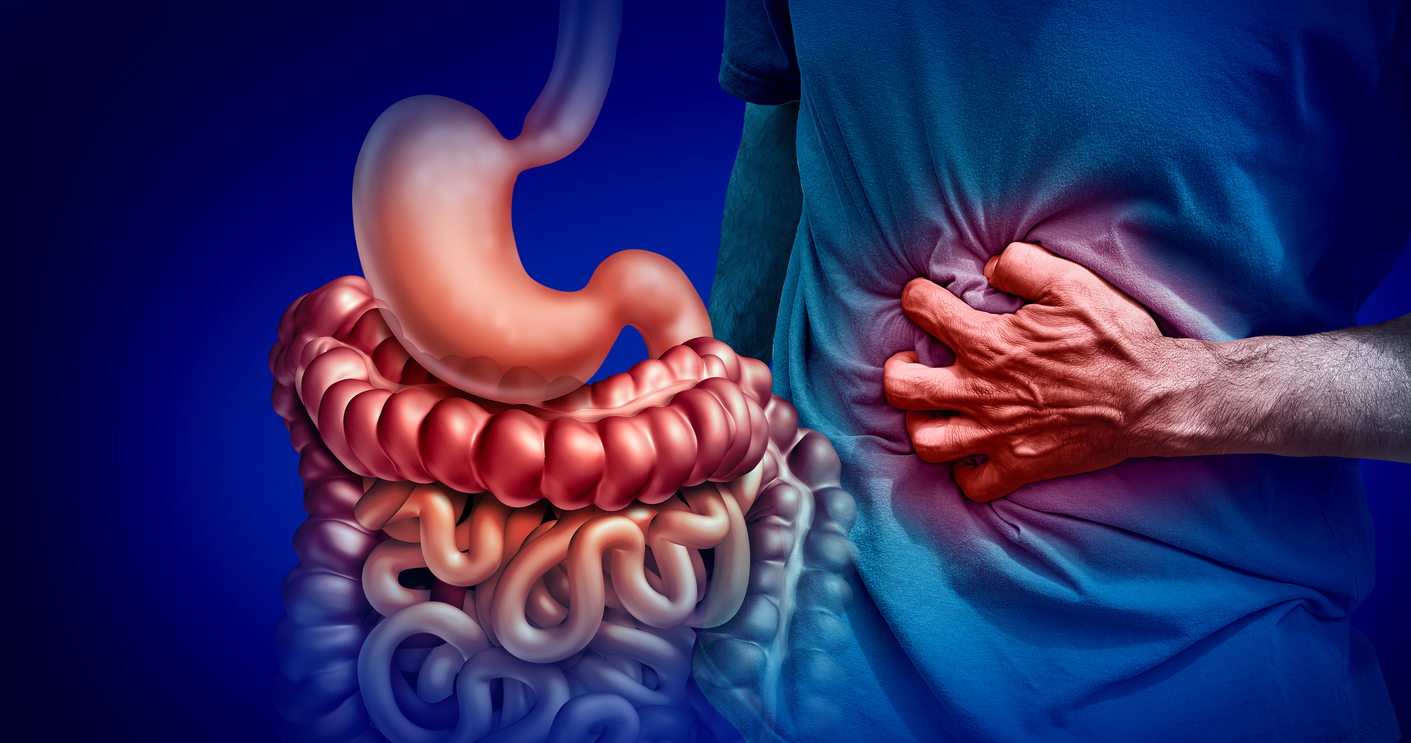
Why You’re Always Bloated: Common Causes and Solutions
Feeling bloated after meals, or even throughout the day, is a common complaint that affects millions of people. Bloating occurs when the abdomen feels full, tight, or swollen, often accompanied by discomfort, gas, or even pain. While occasional bloating is normal, persistent or chronic bloating can indicate an underlying issue that requires attention. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore common causes of bloating, the symptoms to watch for, and practical solutions to relieve discomfort and support digestive health. Understanding these factors can help you take proactive steps to manage bloating and improve overall well-being.
What Is Bloating?
Bloating is the sensation of fullness or swelling in the abdomen. While it can be caused by overeating, temporary digestive slowdown, or gas buildup, persistent bloating may result from dietary habits, digestive disorders, or other medical conditions. Bloating can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status, and may interfere with daily activities, exercise, and sleep.

10 Common Causes of Bloating
Bloating can have multiple causes, ranging from everyday habits to underlying medical conditions. Consider the following top 10 reasons why you might be experiencing bloating:
- Dietary Choices: Foods high in fermentable sugars, such as beans, lentils, broccoli, onions, and certain dairy products, can produce excess gas. Carbonated beverages and sugar alcohols may also contribute to bloating.
- Swallowing Air: Eating quickly, drinking through a straw, chewing gum, or talking while eating can lead to excess air in the digestive tract.
- Constipation: Infrequent bowel movements allow gas to build up behind stool in the colon, increasing abdominal pressure and discomfort.
- Food Intolerances: Lactose intolerance and gluten sensitivity can trigger bloating, gas, and other digestive issues.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): IBS often causes bloating along with abdominal pain and changes in bowel habits, which may worsen after meals.
- Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO): An excess of bacteria in the small intestine can ferment undigested food, producing gas and bloating.
- Hormonal Changes: Women may experience bloating due to fluid retention and digestive changes during their menstrual cycle.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Conditions such as GERD, gastroparesis, ovarian cysts, or fluid retention in the abdomen can contribute to persistent bloating.
- Medications: Certain medications, including antibiotics, pain relievers, or drugs that slow digestion, may lead to gas, bloating, or constipation.
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress can affect gut motility and hormone levels, increasing bloating, discomfort, and digestive disturbances.
10 Symptoms Linked to Bloating
Bloating can present in a variety of ways, ranging from mild discomfort to noticeable physical changes. Consider the following top 10 symptoms that may indicate you’re experiencing bloating:
- Abdominal Fullness: A feeling of tightness or pressure in the stomach, often accompanied by discomfort or heaviness.
- Visible Swelling: Your stomach may appear distended or larger than usual, sometimes noticeable in the mirror or through clothing.
- Excess Gas: Frequent burping or passing gas can accompany bloating, caused by trapped air or fermentation in the digestive tract.
- Pain or Cramping: Mild to moderate abdominal pain, spasms, or cramping may occur alongside bloating, often worsening after meals.
- Nausea: A queasy sensation or upset stomach can accompany bloating, sometimes triggered by certain foods or overeating.
- Rumbling or Gurgling: Audible stomach sounds caused by movement of gas or fluid in the intestines may increase during bloating episodes.
- Belching: Frequent or excessive burping can indicate swallowed air or digestive disturbances contributing to bloating.
- Changes in Bowel Habits: Constipation, diarrhea, or irregular bowel movements often occur alongside bloating, especially in digestive disorders.
- Loss of Appetite: Feeling full quickly or discomfort after eating small amounts can be a symptom of bloating.
- Tight Clothing or Discomfort: Bloating may make pants, belts, or waistbands feel uncomfortably tight, highlighting abdominal distension.
10 Strategies to Help Relieve Bloating
Managing bloating often requires a combination of dietary adjustments, lifestyle changes, and targeted strategies to support healthy digestion and reduce discomfort. Here are 10 effective ways to help relieve and prevent bloating:
- Modify Your Diet: Reduce high-FODMAP foods if sensitive, limit carbonated drinks, and avoid artificial sweeteners that trigger gas.
- Eat Mindfully: Chew food thoroughly, eat slowly, and control portion sizes to reduce swallowed air and improve digestion.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water supports digestion, prevents constipation, and can help relieve bloating.
- Exercise Regularly: Activities like walking, yoga, or light cardio help move gas through the digestive system and promote bowel regularity.
- Manage Stress: Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness can reduce stress-related digestive discomfort.
- Consider Probiotics: Fermented foods or probiotic supplements may help restore healthy gut bacteria and improve overall digestive function.
- Address Constipation: Increase dietary fiber, remain physically active, and use gentle stool softeners if needed to ease bloating.
- Limit Sodium Intake: Reducing salt can help prevent water retention, which contributes to bloating and abdominal discomfort.
- Track Food Triggers: Keeping a food diary can help identify specific foods or beverages that consistently cause bloating.
- Seek Medical Evaluation: Persistent, severe, or worsening bloating should be assessed by a healthcare professional with tests like blood work, stool analysis, imaging, or breath tests to determine the underlying cause.

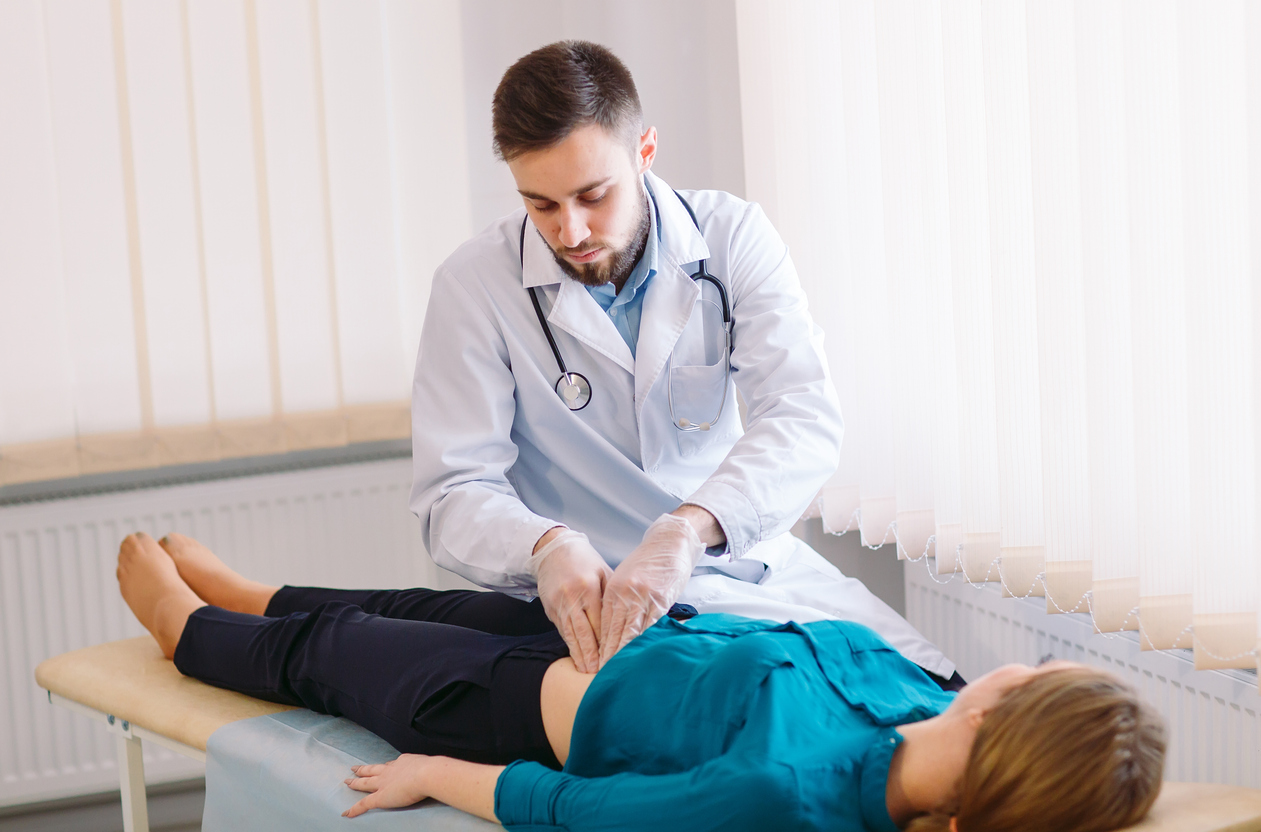
When to See a Doctor
While occasional bloating is common and often related to diet or lifestyle, persistent or severe bloating may signal an underlying health issue that requires medical attention. You should consider seeing a doctor if you experience bloating accompanied by significant abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, blood in your stool, chronic constipation or diarrhea, or if the bloating interferes with daily activities. A healthcare professional can perform a thorough evaluation, including physical exams, imaging, and lab tests, to identify the cause and recommend appropriate treatment. Early assessment helps prevent complications, ensures proper management, and can provide relief more quickly.
Contact Us
Persistent or recurring bloating can interfere with daily life and may signal underlying digestive issues that require attention. By identifying the causes, monitoring symptoms, and implementing effective management strategies — including dietary changes, lifestyle adjustments, and professional guidance — you can take control of your digestive health. If bloating continues despite home measures, it’s important to seek expert evaluation. Schedule a consultation with GastroMD today to receive personalized care, accurate diagnosis, and targeted treatment plans to help you feel comfortable, energized, and healthy again.



