
Everything to Know About Colon Cancer
Colon cancer, or colorectal cancer, is a prevalent disease affecting men and women worldwide. As the third most common cancer diagnosed in the United States, early detection and treatment are essential to prevent this disease. Here we’ll cover everything you need to know about colon cancer, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and various treatment options.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of colon cancer remains unknown, but several factors have been identified as increasing the risk of developing the disease. These factors include:
- Age: Most colon cancer cases occur in people over 50. But it can also develop in younger individuals.
- Family history: Those with a family history of colon cancer or polyps have a higher risk of developing the disease.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Conditions such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis may increase the risk of colon cancer.
- Diet: A diet high in red and processed meats and low in fruits, vegetables, and fiber has been linked to an increased risk of colon cancer.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of colon cancer and the likelihood of dying from the disease.
- Smoking and alcohol consumption: Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are associated with an increased risk of colon cancer.
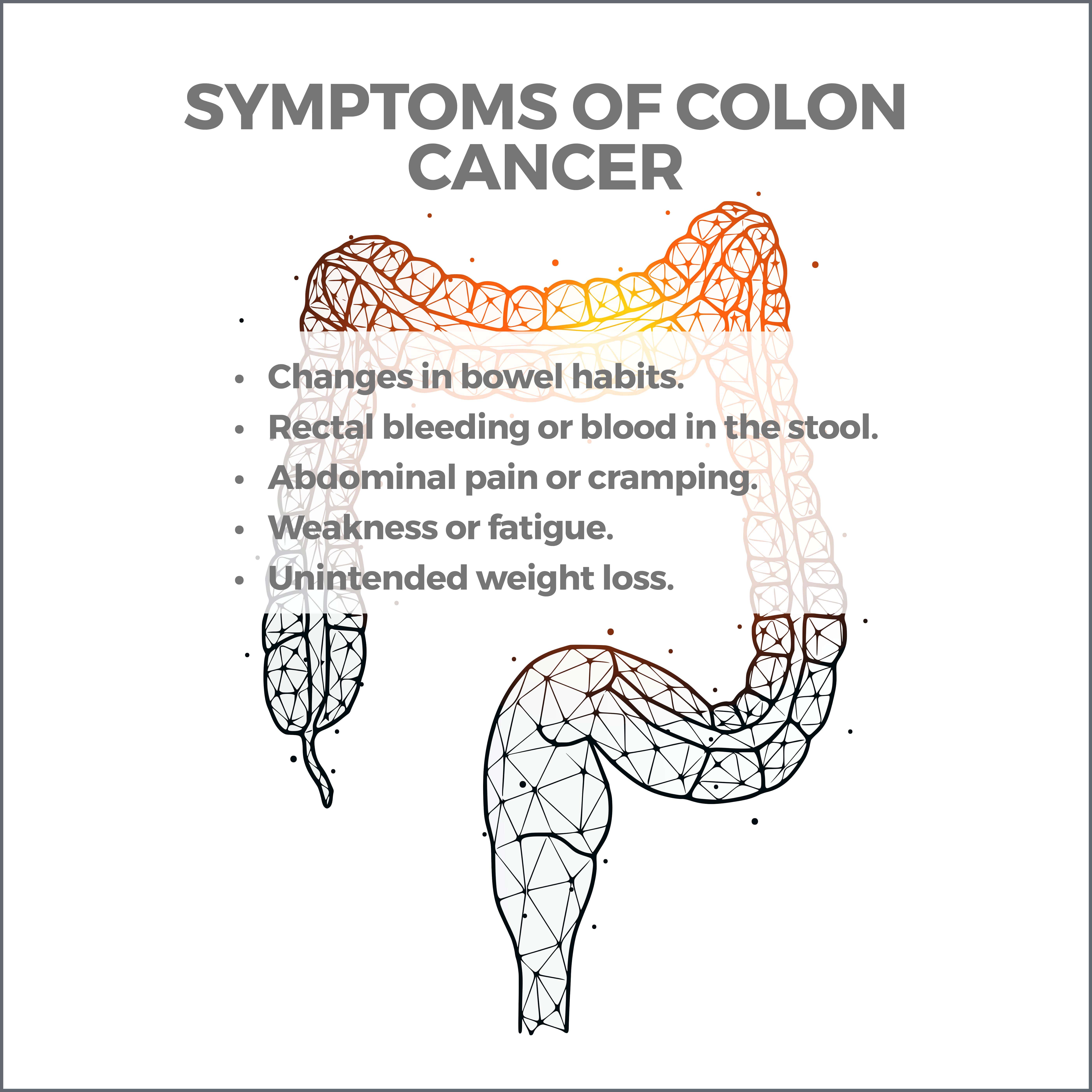
What Are the Symptoms of Colon Cancer?
Colon cancer often begins as small, noncancerous polyps that, over time, can develop into cancer. In its early stages, colon cancer typically presents no symptoms. As the disease progresses, symptoms can include:
- Changes in bowel habits: Diarrhea, constipation, or a change in stool consistency lasting for more than a few weeks can indicate colon cancer.
- Rectal bleeding or blood in the stool can manifest as bright red or dark-colored blood and should be reported to your gastroenterologist.
- Abdominal pain or cramping: Persistent pain or abdominal discomfort can indicate colon cancer.
- Weakness or fatigue: Unexplained tiredness or weakness that does not improve with rest can be a disease symptom.
- Unintended weight loss: Losing weight without changes to diet or exercise habits is a cause for concern and should be investigated.
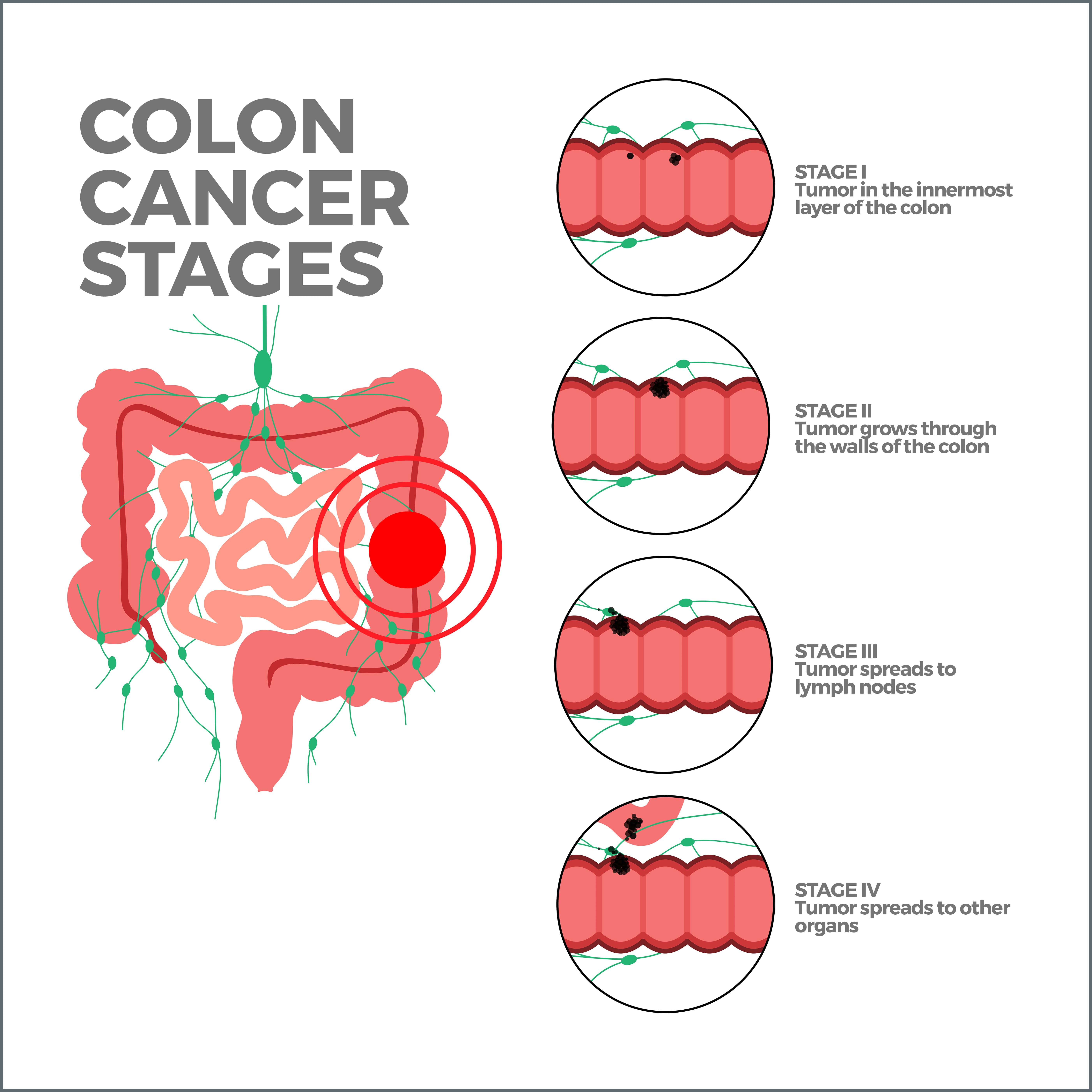
Diagnosing Colon Cancer
Early detection of colon cancer is essential for successful treatment. Several screening methods can help detect colon cancer or precancerous polyps:
- Colonoscopy: A colonoscopy allows a doctor to examine the entire colon and rectum for polyps or cancerous growths. If polyps are found, they can be removed during the procedure, preventing them from developing into cancer.
- Sigmoidoscopy: This test examines the lower part of the colon, known as the sigmoid colon, and the rectum for abnormalities.
- Fecal occult blood test (FOBT) or fecal immunochemical test (FIT): These tests check for blood in the stool, which can indicate colon cancer.
- CT colonography: Also known as virtual colonoscopy, this test uses X-rays and computer technology to create detailed images of the colon and rectum, allowing doctors to detect polyps or cancer.
- Biopsy: If an abnormality is detected during the above tests, a biopsy may be performed to collect tissue samples for further examination under a microscope to determine if cancer is present.

Treatments for Colon Cancer
Treatment options for colon cancer depend on the stage of the illness, its location, and the patient’s overall health. The main treatment options include:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor and surrounding tissue is the most common treatment for colon cancer. Depending on the size and location of the tumor, a surgeon may perform a colectomy (removal of part of the colon) or a local excision (removal of the tumor and a small amount of surrounding tissue).
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells and stop them from dividing. It may be administered orally or through injections and is often used after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells. In some cases, chemotherapy may be used before surgery to shrink the tumor, making removing it easier.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or prevent them from growing. It is often used together with chemotherapy, especially for rectal cancer or when cancer has spread to nearby organs.
- Targeted therapy: These drugs specifically target cancer cells without harming normal cells. Targeted therapy may be used alone or in combination with chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells. Certain types of immunotherapies can be used to treat advanced colon cancer that has not responded to other treatments.
- Palliative care: For patients with advanced colon cancer, palliative care focuses on relieving symptoms and improving quality of life. This may include pain management, nutritional support, and other supportive therapies.
Colon Cancer Prevention Tips
Here is a list of colon cancer prevention tips:
- Maintain a healthy diet: Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, which are high in fiber and essential nutrients. These foods can help promote regular bowel movements and support overall colon health. You should also reduce the consumption of red meats (beef, pork, and lamb) and processed meats (like hot dogs, sausages, and deli meats), as they have been linked to an increased risk of colon cancer.
- Stay physically active: Engaging in regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and supports overall digestive health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week. Excess body weight, particularly around the waist, has been associated with an increased risk of colon cancer. Strive to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Moderate your alcohol intake, as excessive alcohol consumption has been linked to an increased risk of colon cancer. The American Cancer Society recommends no more than one drink per day for women and two for men.
- Quit smoking: Tobacco use increases the risk of various cancers, including colon cancer. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk.
- Get screened: Regular colon cancer screening is essential for early detection and prevention. Screening tests, such as colonoscopies or fecal tests, can help identify precancerous polyps or detect cancer early when treatment is more effective. Talk to your gastroenterologist about the appropriate screening schedule based on your age, family history, and other risk factors.
- Know your family history: If you have a family history of colon cancer or certain inherited syndromes, such as Lynch syndrome or familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), you may be at a higher risk. Discuss your family history with your gastroenterologist to determine appropriate screening measures and risk reduction strategies.
Remember that while these prevention tips can help reduce the risk of colon cancer, they cannot guarantee complete protection against the disease. Regular checkups and open communication with your gastroenterologist are essential for maintaining your overall health and addressing any concerns about your colon cancer risk.
Contact Us
If you have experienced any of the above symptoms or suspect that you may have colon cancer, please do not wait to seek help. At Gastro MD, we help patients identify and battle cancer effectively. Our renowned doctors offer compassionate, innovative treatment.
Contact us today! The team of professionals at GastroMD looks forward to working with you. We are one of the leading gastroenterology practices in the Tampa Bay area. We perform a host of diagnostic procedures using state-of-the-art equipment in a friendly, comfortable, and inviting atmosphere where patient care is always a top priority!



