
Diarrhea
Few occurrences prove as uncomfortable and nerve-wracking as a bout of diarrhea. You have likely experienced diarrhea several times in your life and will probably encounter it on several future occasions.
Overview
Diarrhea is medically defined as the occurrence of loose and watery bowel movements. Typically, you are considered to have diarrhea if you experience at least three or more such events within 24 hours.
Diarrhea is a common health issue. Medical researchers estimate that the problem impacts roughly 180 million people in the United States annually.
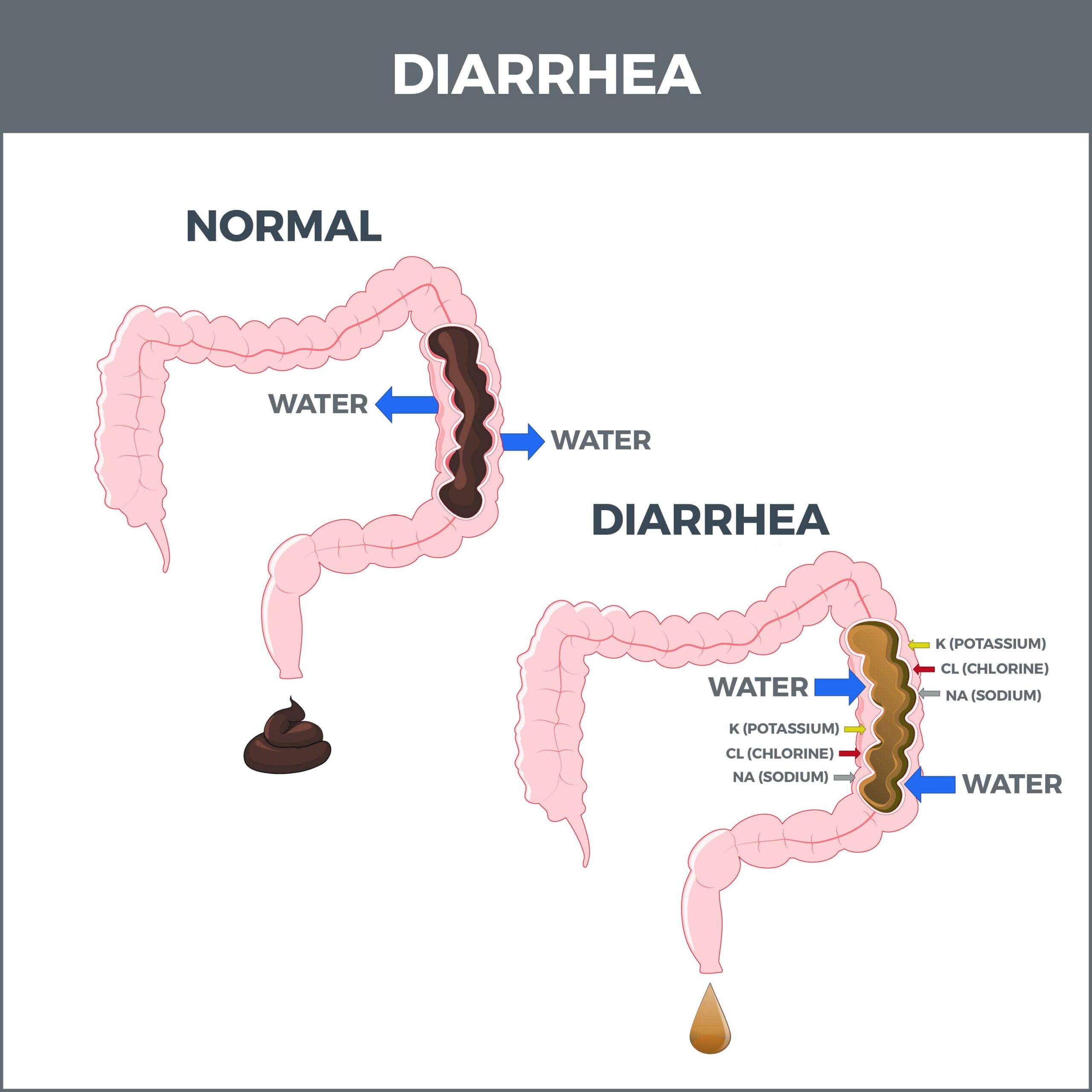
Types Of Diarrheas
Diarrhea is a broad term. It is further divided into sub-categories:
- Acute: Doctors define acute incidents as bouts lasting two weeks or less. In most cases, acute diarrhea results from a relatively mild to moderate and short-lived cause that dissipates on its own or with limited medical intervention.
- Chronic: Chronic or persistent diarrhea involves cases lingering for four weeks or longer. In many such events, the cause is a more serious underlying condition that needs more aggressive treatment.
Causes
Diarrhea has many causes. These factors can be biological, environmental, or related to your lifestyle and might include:
- The medications you regularly take.
- Diet.
- Cigarette smoking and excessive alcohol intake.
- Any number of digestive disorders.
- Food allergies.
- Pathogens like bacteria and viruses.
- Systemic hormonal imbalances.
- Response to chemotherapy or radiation treatments.
The condition can also result from stress. Continual tension and worry often cause a negative influence on digestive tract function.

Symptoms
The primary symptom of diarrhea is the presence of loose and usually watery stools. In more serious cases, you might excrete such waste many times in rapid succession.
Diarrhea can produce other notable physical symptoms such as:
- Abdominal pain.
- Bloating.
- Gas.
- Burping.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
In cases of a systemic infection, you might also experience untoward events like chills, an elevated body temperature, and fatigue.
Complications
In severe acute or long-lasting chronic incidents, potentially serious complications may emerge. Arguably, the most serious issue is dehydration.
You lose significant amounts of fluids and essential nutrients like electrolytes when you have diarrhea. These substances are needed to help your body function at an optimal level. Failing to replenish them can lead to more significant illnesses or possibly even death.
Symptoms of dehydration include increased thirst, decreased urine output, excessive tiredness, dizziness or unsteadiness, and dry mouth. If you have diarrhea and experience these symptoms, it is important to drink as much water as you can and replenish lost electrolytes.
Diagnosis
It is crucial to realize that diarrhea is not a disease but a symptom of some specific underlying cause. Severe cases or those lingering for extended periods or accompanied by other alarming events should be evaluated by your gastroenterologist as soon as possible.
Diagnosing the issue can prove time-consuming and require several steps.
The first phase typically involves a thorough physical examination. During this process, your doctor will likely ask you several information-gathering questions, including:
- When did your diarrhea begin?
- Are you experiencing any other symptoms?
- Are you dealing with high-stress levels?
- Did you travel to a foreign nation and consume water there?
- What foods typically comprise your diet?
- Do you smoke or drink alcohol with relative frequency?
- What type of medications do you regularly ingest?
Once this process is completed, your medical professional may offer a visual investigation of your abdominal region to identify any growths or abnormalities capable of causing diarrhea.
During later stages of the investigative process, your doctor might perform various diagnostic tests to identify its cause. Such efforts may include blood tests, stool samples, and other tests designed to measure your intolerance to specific foods or the chemicals found in them.
If your physician believes medication could be the cause, they might reduce the dosage of the drug or prescribe another alternative.
Occasionally, your doctor might order internal imaging tests. Standard procedures include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computerized tomography (CT scans). They enable physicians to observe internal components like organs and tissues. Certain diarrhea-inducing causes can be identified through the revealed images.
Sometimes, doctors use tests like sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy. Like MRI and CT scans, these diagnostic techniques provide internal images of the colon and other digestive tract regions.
Potential Treatment Options
Specific treatments depend on the diarrhea-inducing problem. Addressing them can result in a decrease in or the elimination of incidents.
In many instances, mild occurrences resolve independently without significant effort. The use of over-the-counter diarrhea-stopping medications can also lessen uncomplicated cases. Other common treatment options include:
- Identifying Food Allergies and Altering Diet: Occasional incidents might be avoided by identifying food allergies or intolerance or changing your diet. Particularly fatty and spicy foods can irritate the digestive system, sometimes resulting in diarrhea.
- Antibiotics: Certain cases of diarrhea brought forth by bacterial infections might be slowed by administering antibiotic drugs. In eradicating the offending pathogen, symptoms like diarrhea are often alleviated.
- Changing Dosage or Adjusting Medications: Certain therapeutic drugs could prove abrasive to the digestive system. Bouts of diarrhea caused by such substances may be lessened or eliminated by making dosage adjustments or finding a comparable medication.
- Reducing Stress: Occasionally, limiting stress might reduce incidents of diarrhea. By participating in productive stress-busting activities, you release tension and potentially prevent it from causing physical symptoms.
When Should You See a Doctor?
It is important to understand that most cases of diarrhea result from simple, resolvable issues that pass in a few days or weeks. You should strongly consider visiting your gastroenterologist under circumstances when:
- Diarrhea is accompanied by severe pain.
- You notice the presence of blood, pus, or undigested food in stools.
- You have a fever of 101 degrees or higher.
- You experience the symptoms of dehydration.
Above all, you are firmly encouraged to consult with your doctor if diarrhea lasts for longer than a week, worsens, or tends to recur for no apparent reason.

Recovery
Medical professionals are often reluctant to offer specific recovery times because time frames hinge on the underlying medical issue, the disorder’s severity, your age and overall health, and your response to the particular treatment employed.
Prevention
Cases caused by underlying illnesses may not always be preventable. You might decrease your risk of uncomplicated cases through efforts including:
- Observing Appropriate Hygienic Practices: Many cases of diarrhea are precipitated by pathogens collecting on dirty surfaces and improperly prepared food. Simply washing your hands after they come into contact with frequently touched surfaces and preparing food following instructions can kill most diarrhea-causing bacteria. Wash fresh vegetables to eliminate potentially hazardous pesticides.
- Using Caution When Visiting Foreign Countries: Countries in the developing world might not have the technology to create proper filtration systems for public water supplies. They could grow contaminated with any number of pathogens or parasites. You are urged to refrain from drinking publicly dispensed water in these locations.
- Watching Your Diet: The digestive tract can sometimes be sensitive to excessively fatty, spicy, or processed edibles. You should limit your intake of such products.
- Limiting Potentially Detrimental Vices: If you drink alcohol, it should be undertaken in moderation. Chemicals in cigarettes and tobacco products can inflame the digestive tract lining and should be avoided.
Contact Us
Contact us today! The team of professionals at GastroMD looks forward to working with you. We are one of the leading gastroenterology practices in the Tampa Bay area. We perform many diagnostic procedures using state-of-the-art equipment in a friendly, comfortable, and inviting atmosphere where patient care is always a top priority!



